How Forging Enhances Manufacturability and Strengthens High-End Supply Chains
For high-end equipment components—such as transition sections, marine bearing rings, gear parts, and adapter rings—successful manufacturing relies not only on sound design but also on how effectively that design can be transformed into high-quality, cost-efficient products in real production.
To achieve this, design for manufacturability (DFM) becomes a key principle. This article explores the value of DFM and how forging plays a critical role in strengthening supply chain resilience.
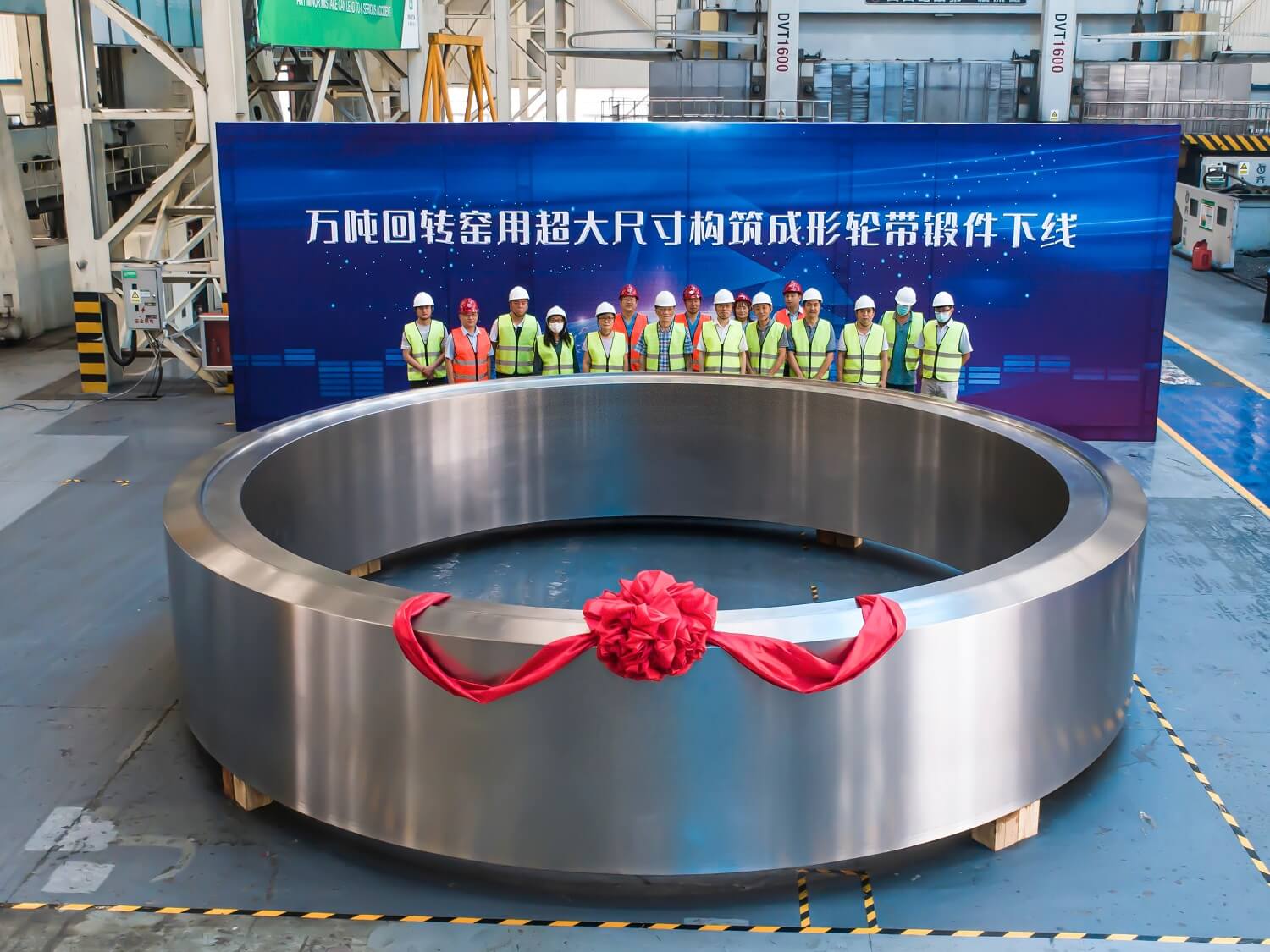

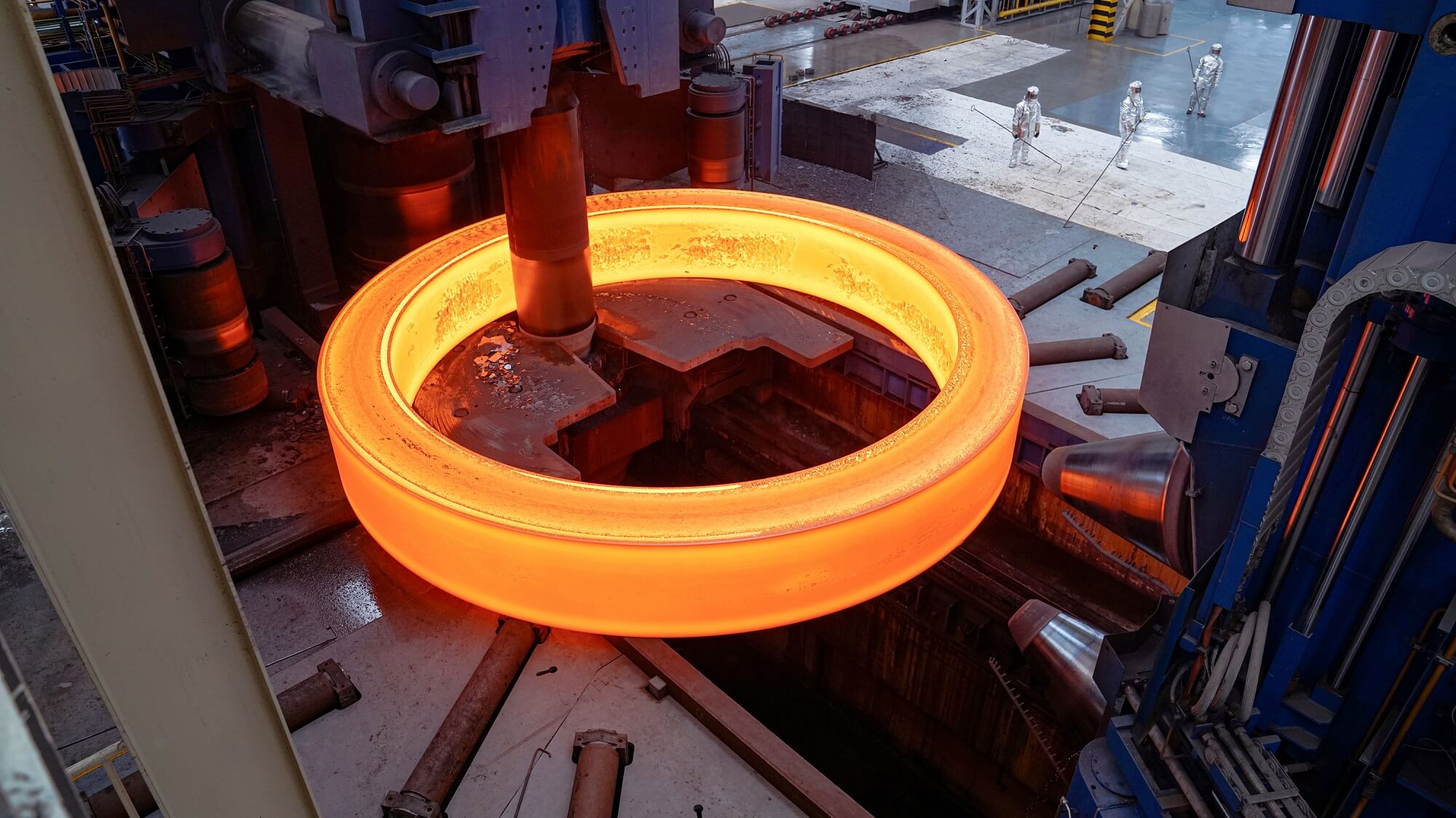
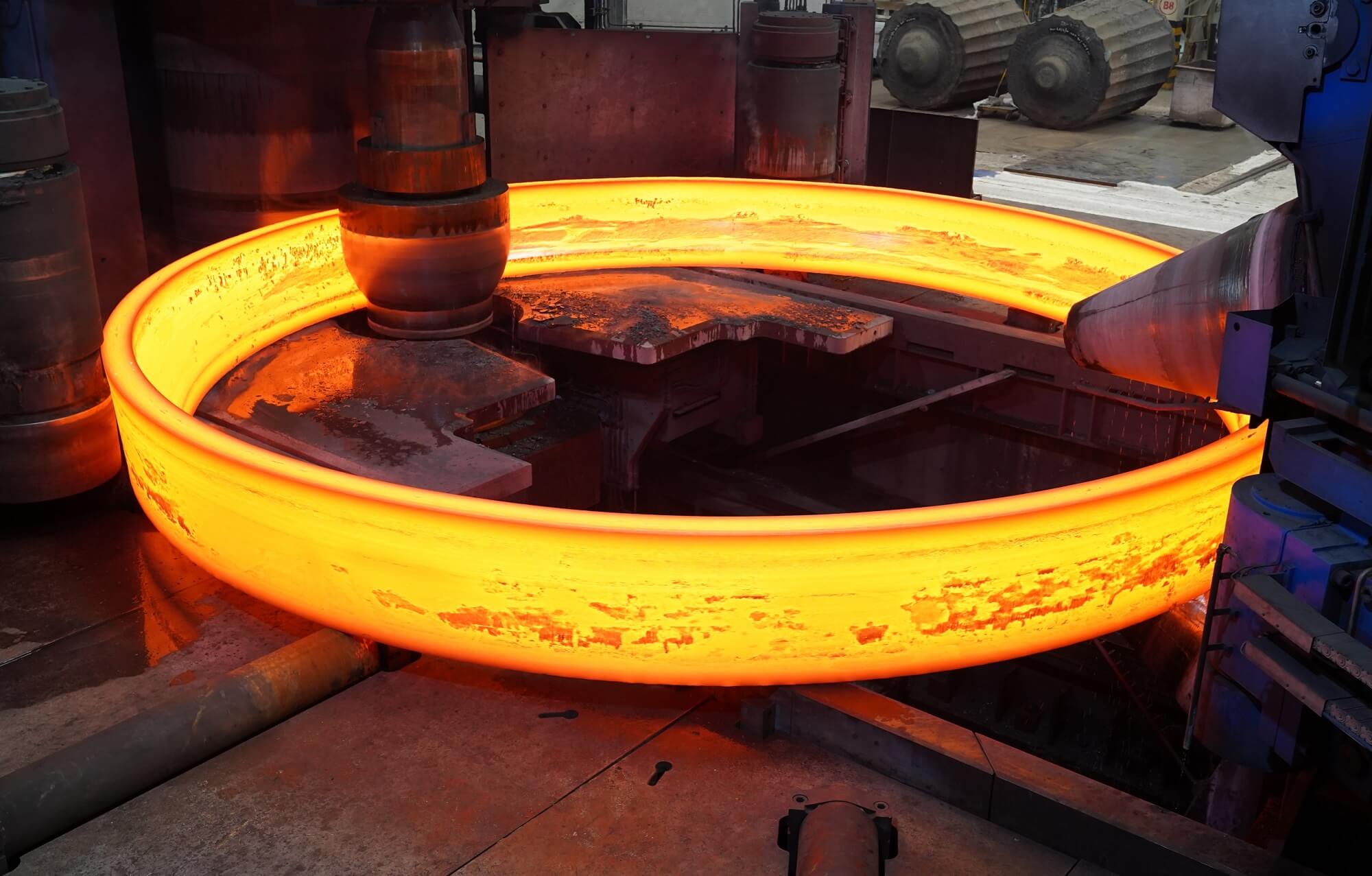
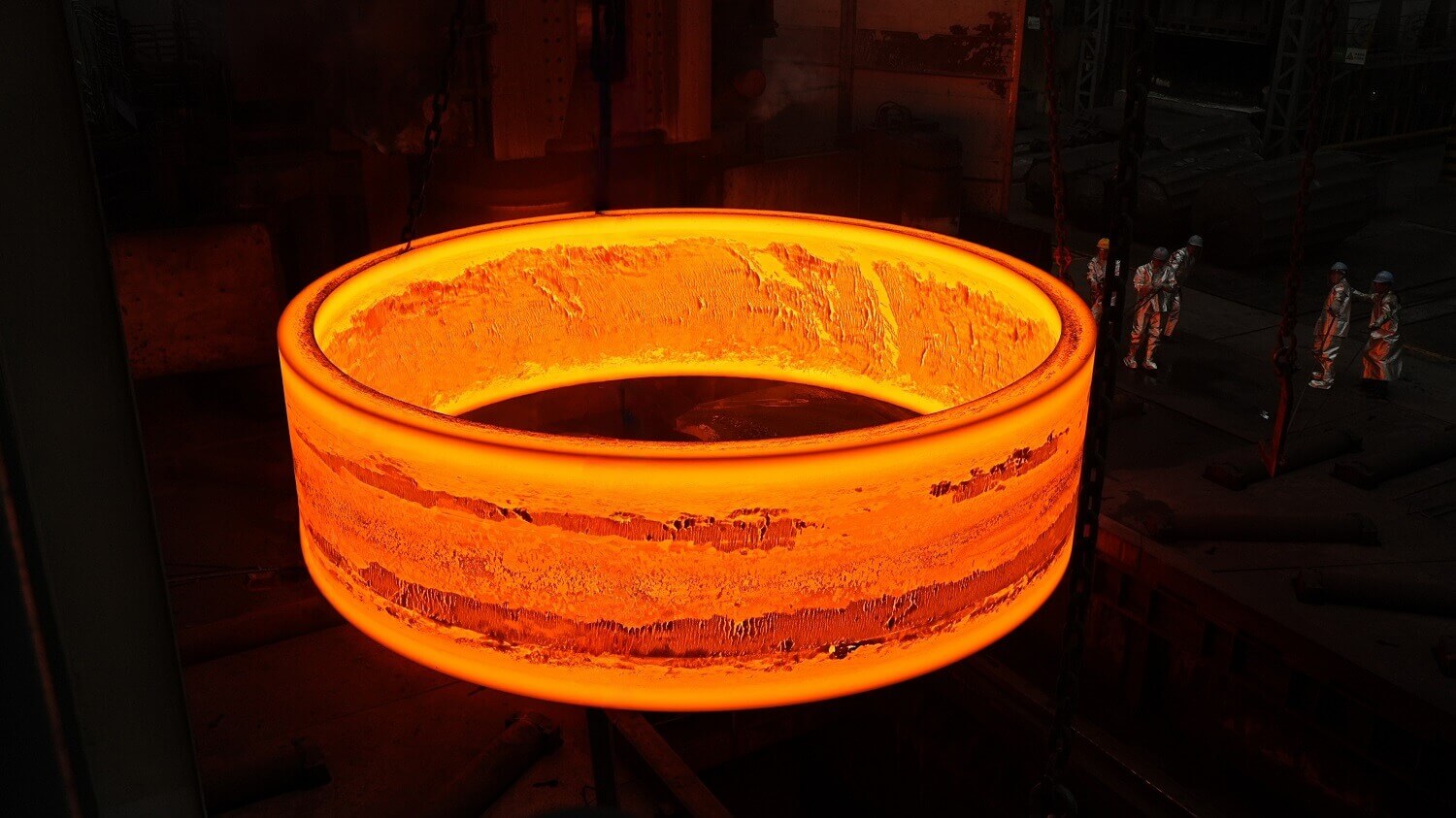
A 170-ton forged kiln tyre converted from casting to forging production
Design for Manufacturability: Bridging Design and Production
Design for manufacturability is an engineering concept that emphasizes considering production feasibility during the early design stage. By optimizing design layouts and structures, products become easier to process and assemble, while overall efficiency improves.
For manufacturers, applying DFM principles simplifies workflows, reduces costs, stabilizes product quality, and provides a strategic advantage in supply chain management.
Four Core Principles of DFM
Simplify the design:Reduce unnecessary complexity without affecting functionality. Simpler designs make manufacturing and assembly easier, lower the risk of errors, and help cut costs.
Select the right materials:Use readily available materials that fit existing manufacturing processes. The “right” material balances performance, efficiency, and cost—it doesn’t always have to be exotic or rare.
Promote standardization:Standardize part dimensions and production steps where possible. This reduces the need for custom tooling and streamlines supply chain management.
Minimize part count:Integrate components whenever possible. Fewer parts mean fewer assembly steps, lower error rates, and less pressure on procurement and inventory management.
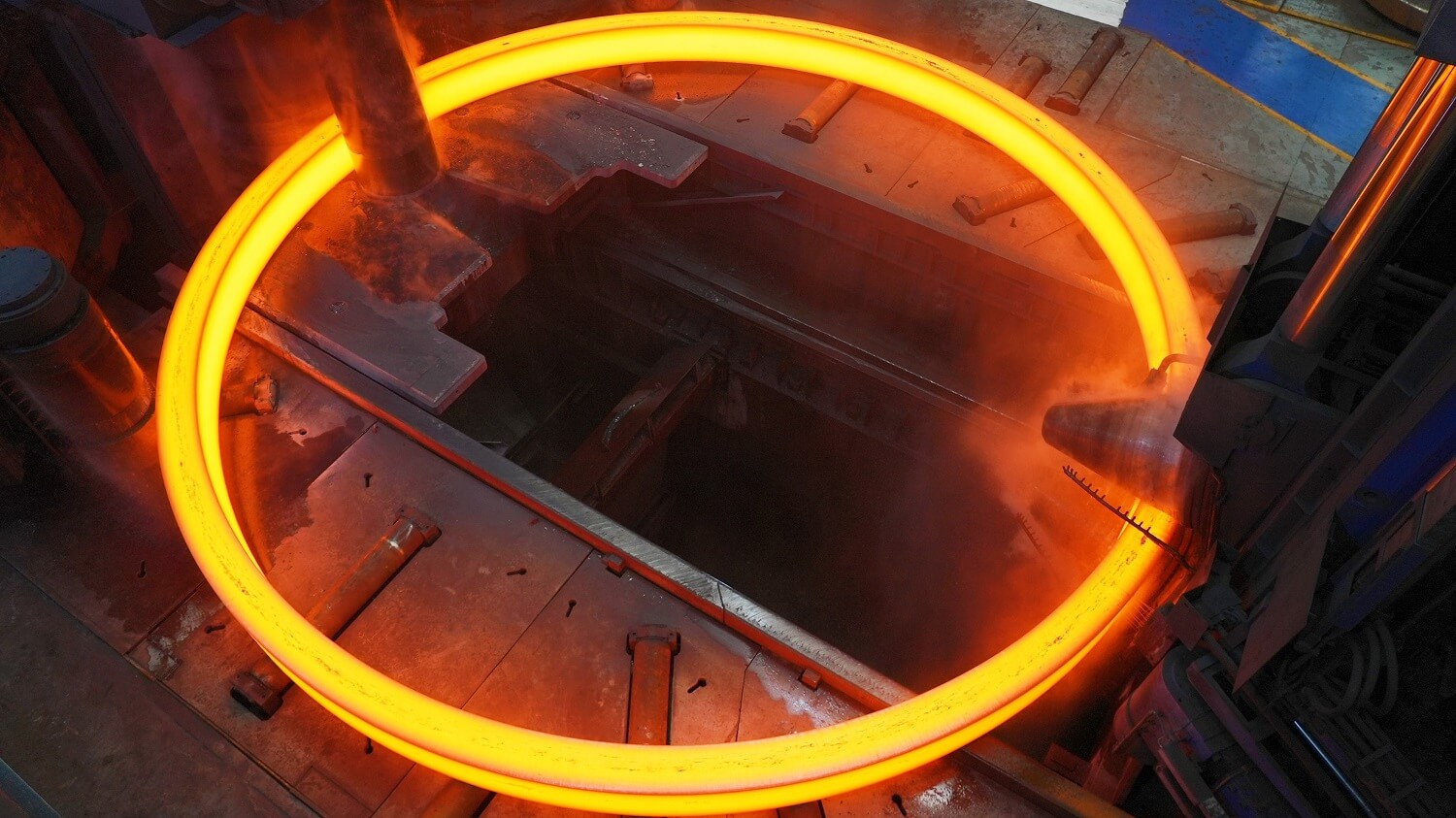

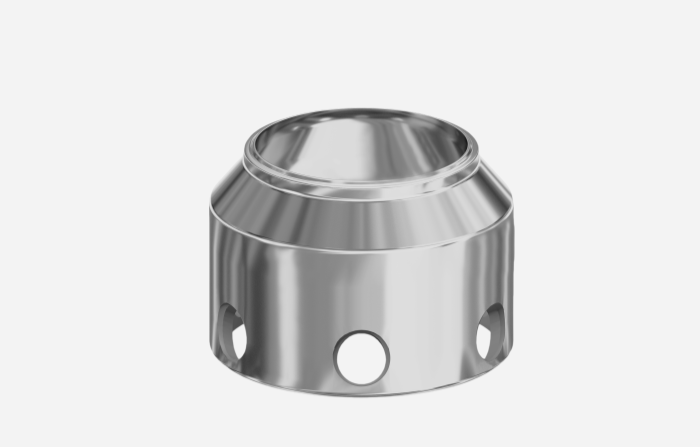
Compared with segmented bearings,
integral bearings offer a longer service life
Forging: The Bridge Between DFM and Supply Chain Resilience
As a critical metal forming process, forging not only supports DFM through its inherent technical advantages but also contributes directly to a more resilient supply chain. Its impact can be seen in five key areas:
1. Enhanced material performance:
Forging greatly improves the strength and structural integrity of metals. Forged components feature superior mechanical properties and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and minimizing the risk of supply disruptions due to part failure.
2. Reduced material waste:
Compared with casting and other processes, forging produces minimal scrap. This aligns perfectly with the DFM principle of efficient resource use—lowering raw material costs and supporting sustainable manufacturing.
3. Stable production quality:
Forging ensures consistency and uniformity across batches. This minimizes the chance of defective parts and production stoppages, keeping the entire supply chain running smoothly.
4. Improved energy efficiency:
Forging is generally more energy-efficient than other metal forming methods. Optimized energy use supports green manufacturing goals and reduces cost fluctuations caused by energy price volatility.
5. Near-net shaping capability:
With advances in open-die forging technology, near-net shape forming is increasingly achievable. This allows forged parts to closely match final dimensions, minimizing subsequent machining—saving both materials and time, especially in large forgings.
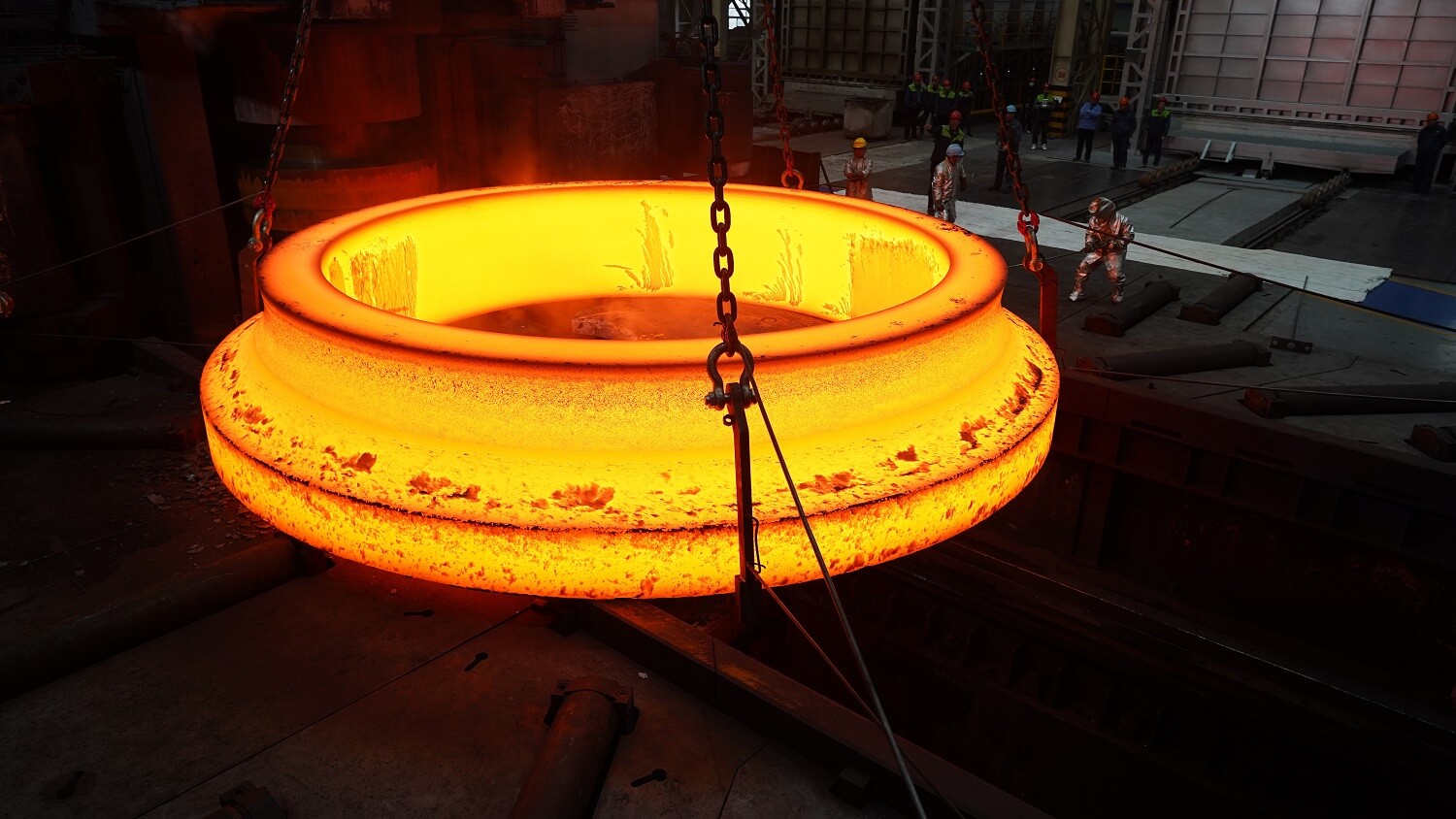

Near-net-shape technology reduces raw material consumption.
In today’s fast-changing manufacturing landscape, design for manufacturability has become a cornerstone of competitiveness. When combined with the inherent strengths of forging, it forms a powerful synergy that supports stable, flexible, and efficient supply chains.
Manufacturers that embrace DFM principles and leverage the advantages of forging can continuously optimize their production processes—building supply chains that are not only efficient but also resilient in the face of future challenges.
Recommended reading

Unlocking the Secrets of Forging: The Performance Code of Classic Processes

Must-Read for Ring Forging: Advantages and Applications of the Forge-Rolling Process

Open-Die Forging vs. Ring Rolling: Helping You Choose the Optimal Forging Process

Unlocking Heat Treatment: How to Make Forgings Stronger, Tougher, and More Reliable

Forging Procurement: Manufacturer Or Middleman?