Unlocking the Secrets of Forging: The Performance Code of Classic Processes
Behind every reliable key component in modern industrial equipment lies a hidden yet critical process—forging.
Forging is not just about “shaping”—it is the process of imbuing metal with strength and toughness, giving components higher strength, better reliability, and longer service life. This is why forging is widely used in energy, transportation, engineering equipment, aerospace, and other high-end industries.
Currently, the mainstream forging processes in global manufacturing can be categorized into four major types: impression die forging (closed-die forging), cold forging, open-die forging, and seamless rolled ring forging.
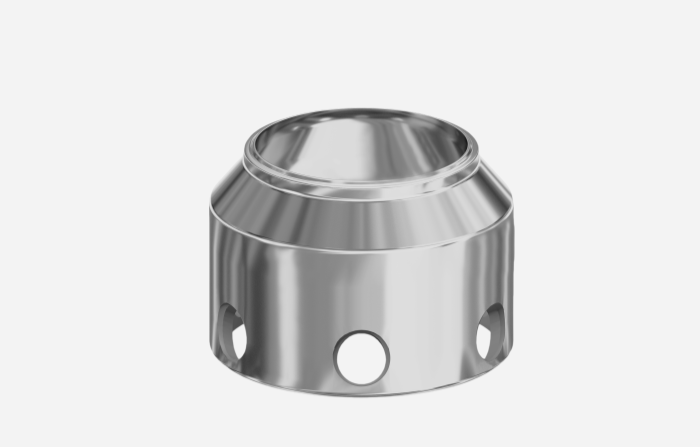
Impression Die Forging
If you need large-scale, rapid production of precision components, impression die forging is the go-to choice.
Also known as closed-die forging, this process uses fully enclosed dies to shape the billet. During processing, the billet is subjected to high pressure, ensuring complete filling of the die cavity to form a precise component. Compared with other methods, impression die forging requires higher pressure to achieve accuracy, making it ideal for mass production of precision parts.
Why Choose Impression Die Forging?
● High material utilization with minimal waste
● Excellent efficiency, perfect for large-scale production
● Enhanced fatigue resistance and impact performance
● Suitable for high strength-to-weight ratio components
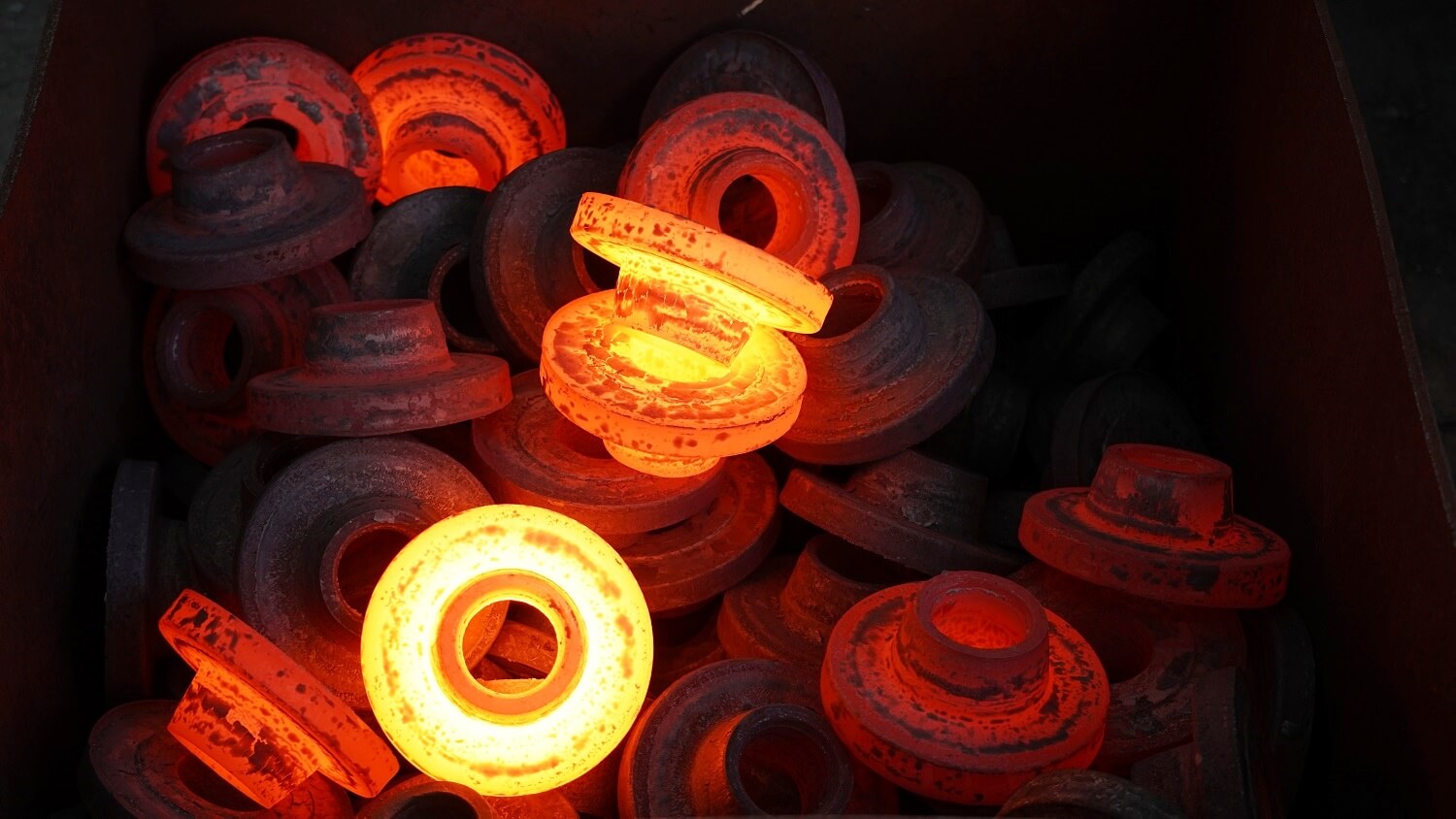

Cold Forging
Looking for smoother surfaces and stricter dimensional accuracy? Cold forging is the answer.
Performed at room or low temperatures without preheating, cold forging is primarily used for producing components with excellent surface quality and strict dimensional tolerances. It is widely applied in shafts, hollow parts, special-shaped components, and cup-like geometries.
Key Advantages of Cold Forging:
● Strict dimensional control and excellent precision
● Smooth surfaces, minimizing post-machining requirements
● High material efficiency with almost zero waste
● Longer die life compared to hot forging, reducing long-term costs
● Significant improvements in yield strength and tensile strength
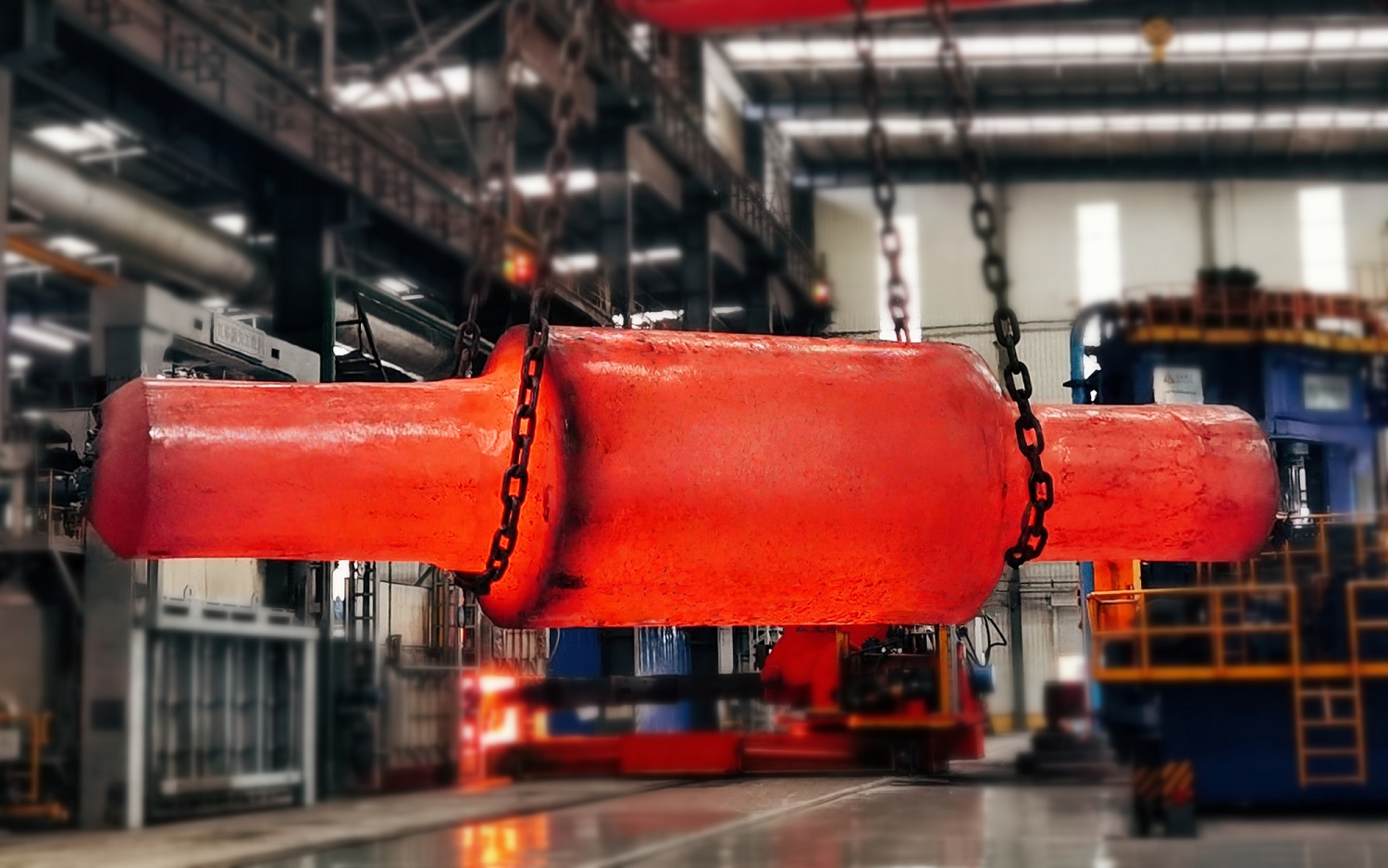
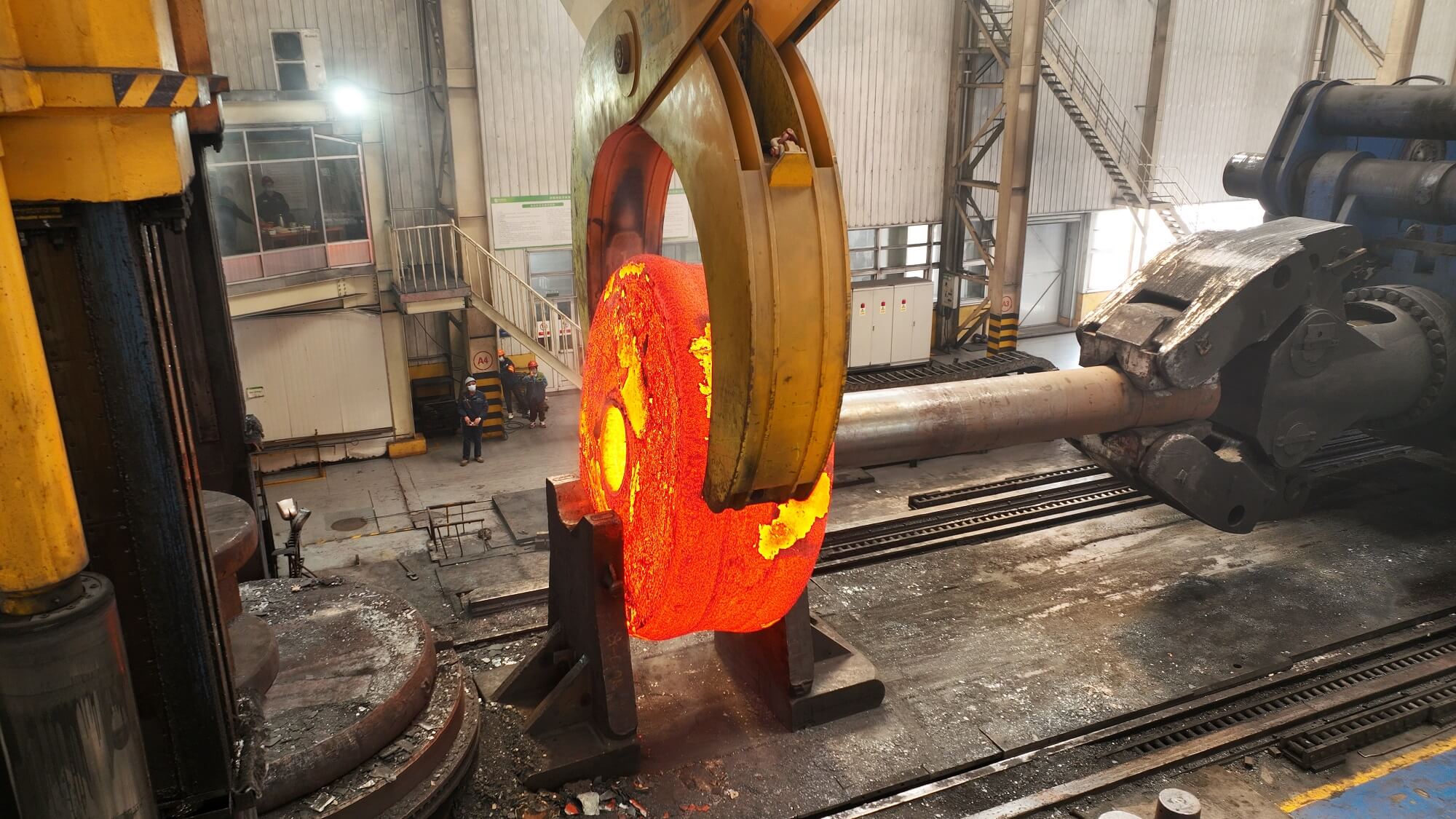
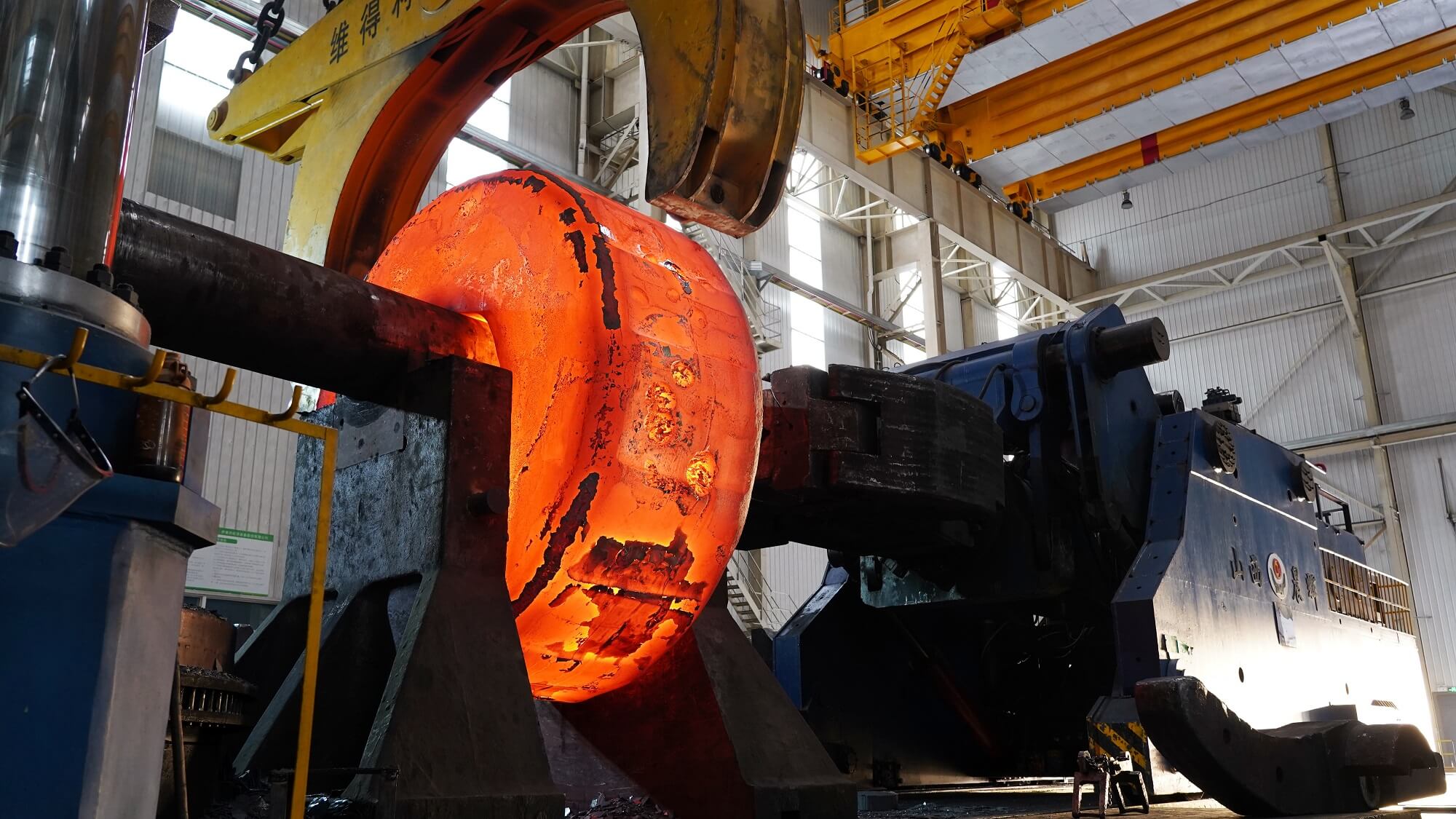
Open-Die Forging
When parts weigh tens or even hundreds of tons, open-die forging is the only option.
Also known as open-die forging, this method plastically deforms billets by directly applying force. The workpiece is placed between flat dies and shaped gradually through repeated hammering. Since the dies do not fully enclose the billet, they serve more as forming tools than closed cavities.
Key Advantages of Open-Die Forging:
● Enhances fatigue resistance and durability
● Maintains continuous grain flow for improved mechanics
● Extends service life, lowering maintenance costs
● Improves overall strength, reducing performance risks
● Minimizes shrinkage cavities and inclusions
● Produces finer, more uniform grains for better overall performance

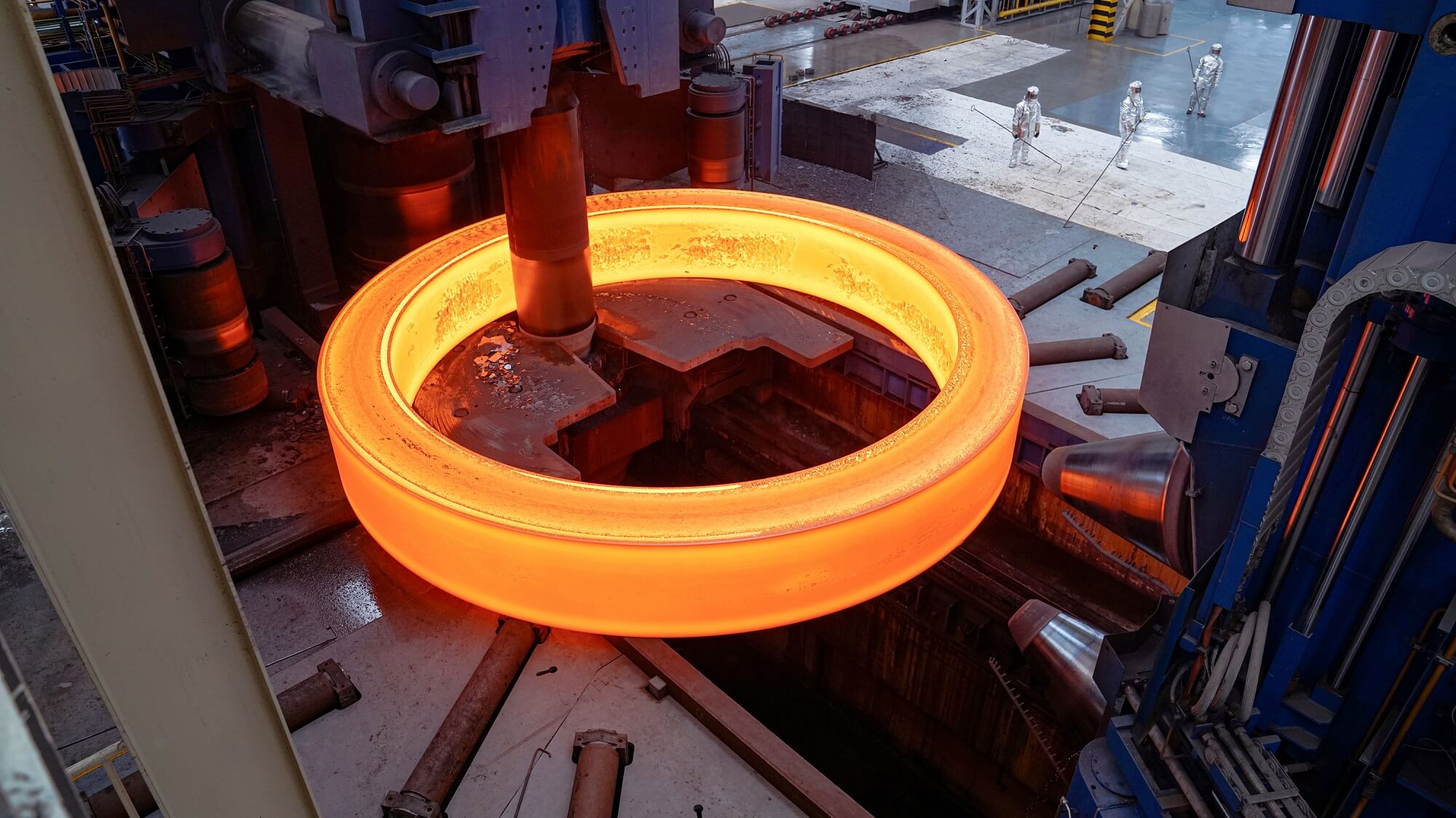
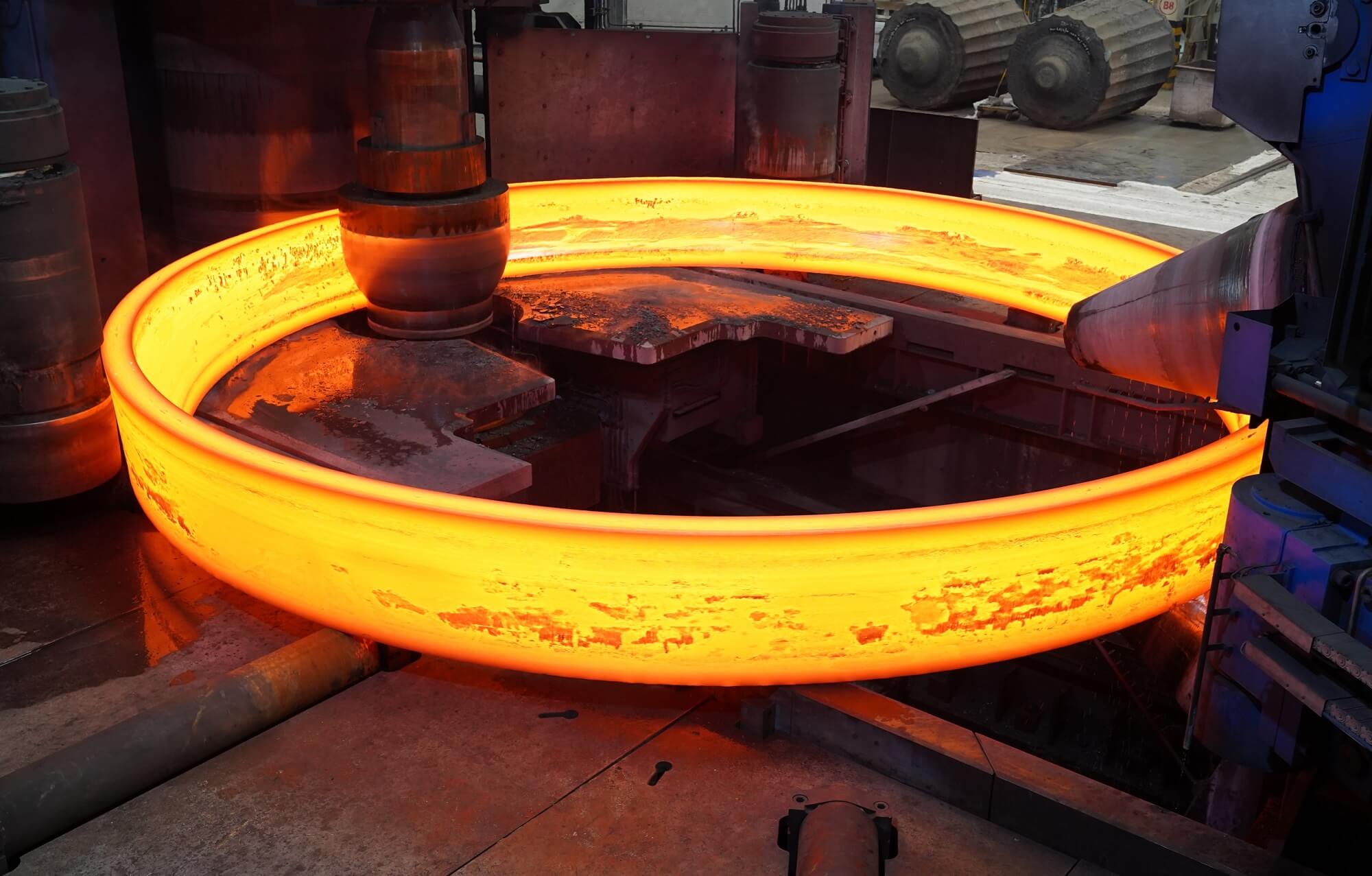
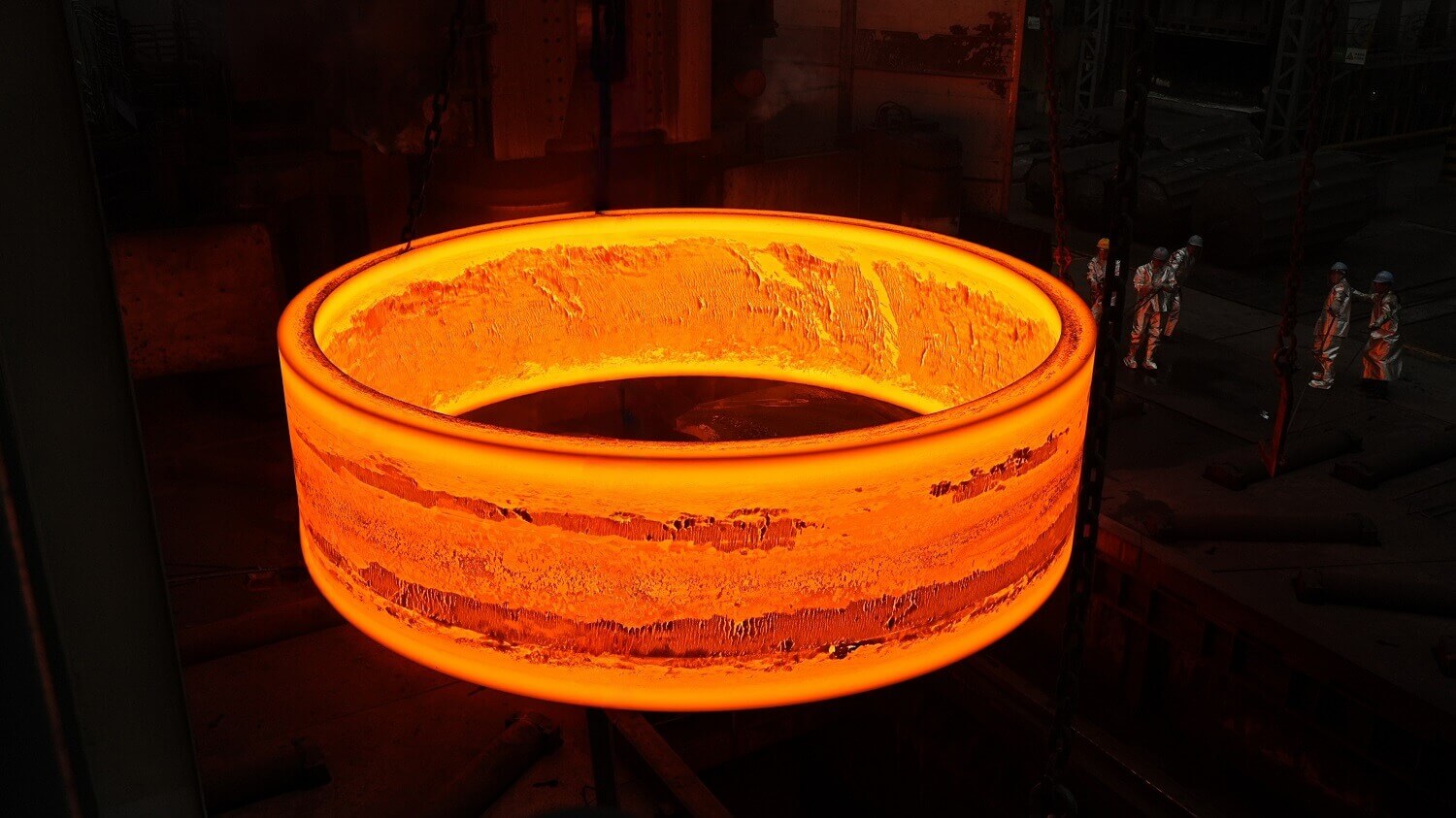
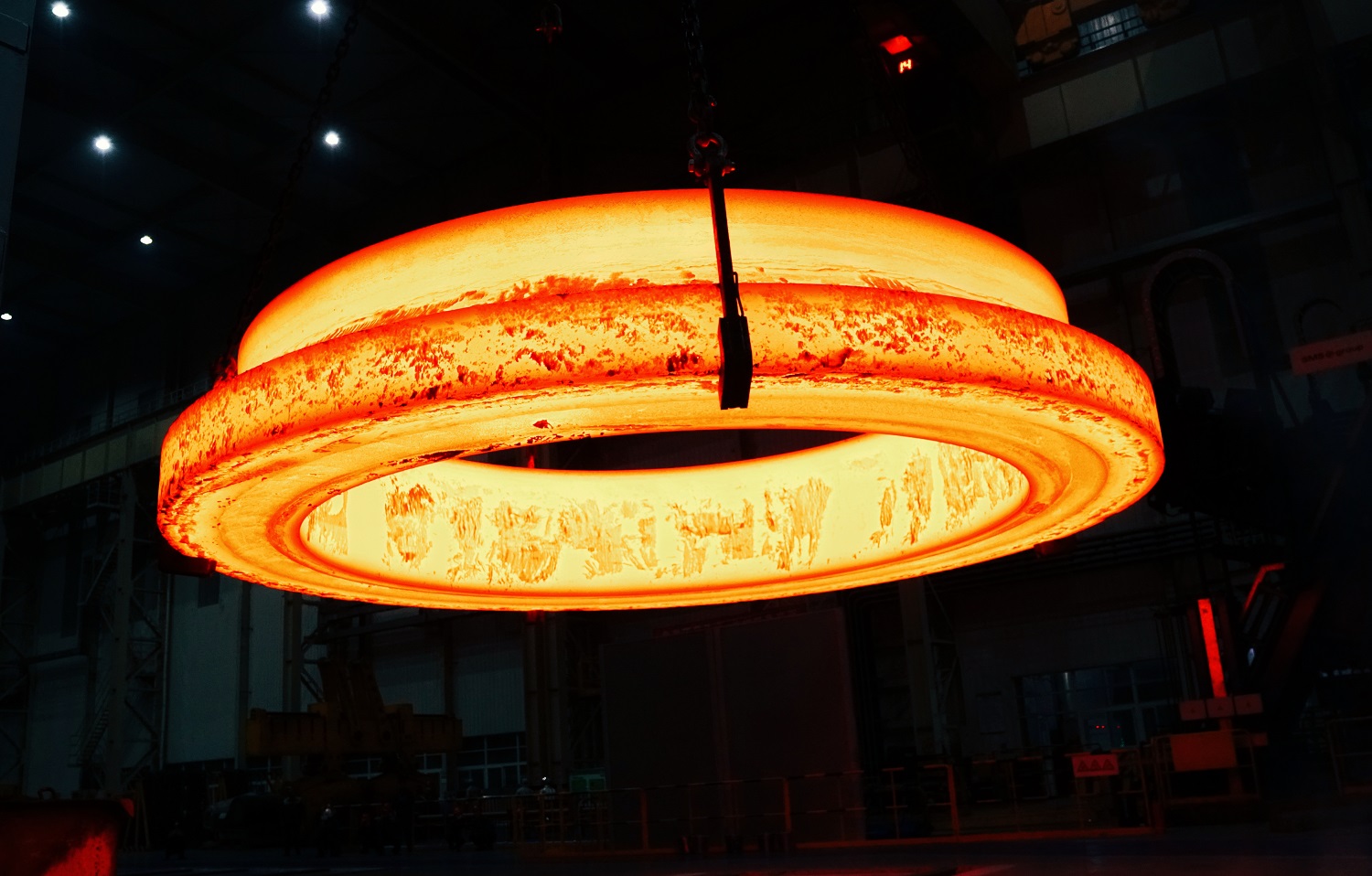
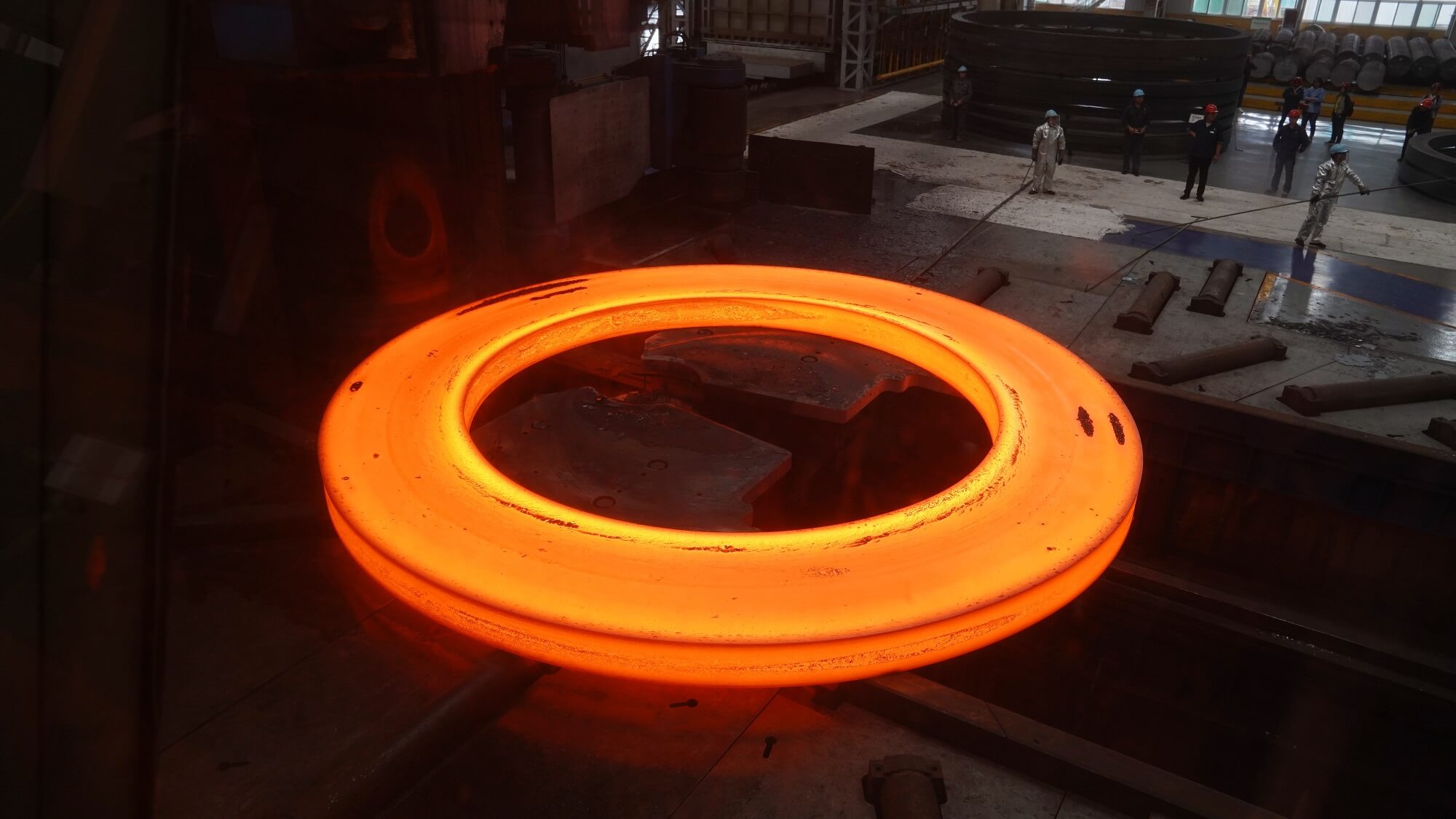
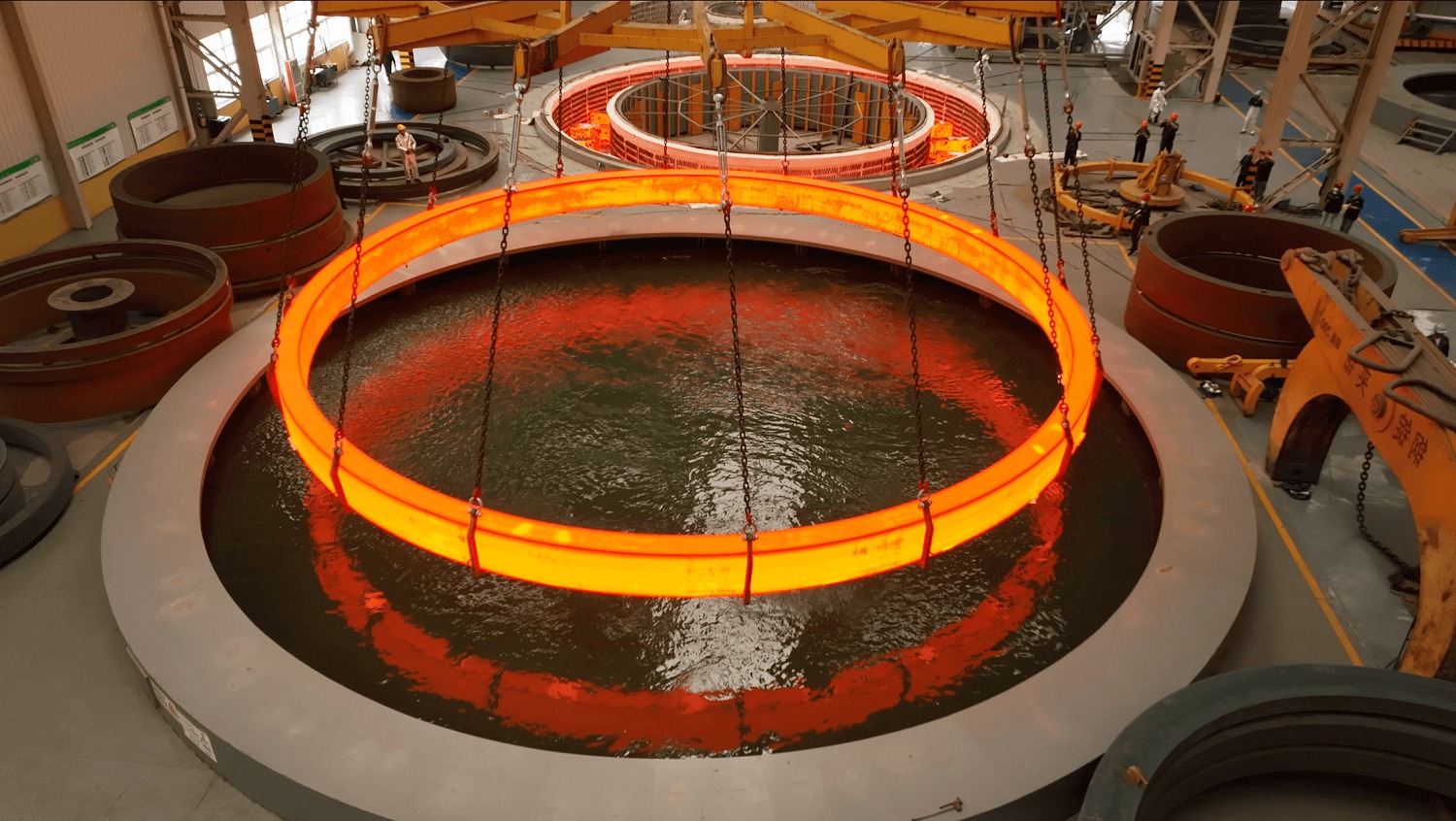
Rolled Ring Forging
For ring-shaped components, seamless rolled ring forging ensures both performance and efficiency.
This process begins with piercing a solid billet, followed by rolling and extrusion to form a thin-walled ring forging. Unlike other methods, seamless rolled ring forging uses curved dies instead of flat dies, making it uniquely suited for ring-shaped parts.
Key Advantages of Rolled Ring Forging:
● Exceptional structural integrity and mechanical reliability
● High overall strength for heavy-load applications
● Controlled grain flow ensures optimal stress distribution
● Eliminates welds, inclusions, and porosity for higher safety

Together, these diverse yet complementary forging processes form the backbone of modern industrial equipment, ensuring reliable operation and extended service life.
If you are still unsure which forging method to choose, bring your requirements to Iraeta. With our extensive industry experience and technical expertise, we can tailor the optimal forging solution for every component—maximizing both performance and reliability.
Recommended reading

Must-Read for Ring Forging: Advantages and Applications of the Forge-Rolling Process

Open-Die Forging vs. Ring Rolling: Helping You Choose the Optimal Forging Process

Unlocking Heat Treatment: How to Make Forgings Stronger, Tougher, and More Reliable

Forging Procurement: Manufacturer Or Middleman?